
| Package | flash.display |
| Class | public final class Graphics |
| Inheritance | Graphics  Object Object |
| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | AIR 1.0 Flash Player 9 |
graphics property that is a Graphics object.
The following are among those helper functions provided for ease of use:
drawRect(), drawRoundRect(),
drawCircle(), and drawEllipse().
You cannot create a Graphics object directly from ActionScript code.
If you call new Graphics(), an exception is thrown.
The Graphics class is final; it cannot be subclassed.
| Method | Defined By | ||
|---|---|---|---|
beginBitmapFill(bitmap:BitmapData, matrix:Matrix = null, repeat:Boolean = true, smooth:Boolean = false):void
Fills a drawing area with a bitmap image. | Graphics | ||
Specifies a simple one-color fill that subsequent calls to other
Graphics methods (such as lineTo() or drawCircle()) use when drawing. | Graphics | ||
beginGradientFill(type:String, colors:Array, alphas:Array, ratios:Array, matrix:Matrix = null, spreadMethod:String = "pad", interpolationMethod:String = "rgb", focalPointRatio:Number = 0):void
Specifies a gradient fill used by subsequent calls to other
Graphics methods (such as lineTo() or drawCircle()) for the object. | Graphics | ||
Specifies a shader fill used by subsequent calls to other Graphics methods
(such as lineTo() or drawCircle()) for the object. | Graphics | ||
Clears the graphics that were drawn to this Graphics object, and resets fill and
line style settings. | Graphics | ||
Copies all of drawing commands from the source Graphics object into the
calling Graphics object. | Graphics | ||
Draws a curve using the current line style from the current drawing position
to (anchorX, anchorY) and using the control point that (controlX,
controlY) specifies. | Graphics | ||
Draws a circle. | Graphics | ||
Draws an ellipse. | Graphics | ||
Submits a series of IGraphicsData instances for drawing. | Graphics | ||
Submits a series of commands for drawing. | Graphics | ||
Draws a rectangle. | Graphics | ||
drawRoundRect(x:Number, y:Number, width:Number, height:Number, ellipseWidth:Number, ellipseHeight:Number = NaN):void
Draws a rounded rectangle. | Graphics | ||
drawTriangles(vertices:Vector.<Number>, indices:Vector.<int> = null, uvtData:Vector.<Number> = null, culling:String = "none"):void
Renders a set of triangles, typically to distort bitmaps and give them a three-dimensional appearance. | Graphics | ||
Applies a fill to the lines and curves that were added since the last call to the
beginFill(), beginGradientFill(), or
beginBitmapFill() method. | Graphics | ||
 |
Indicates whether an object has a specified property defined. | Object | |
 |
Indicates whether an instance of the Object class is in the prototype chain of the object specified
as the parameter. | Object | |
lineBitmapStyle(bitmap:BitmapData, matrix:Matrix = null, repeat:Boolean = true, smooth:Boolean = false):void
Specifies a bitmap to use for the line stroke when drawing lines. | Graphics | ||
lineGradientStyle(type:String, colors:Array, alphas:Array, ratios:Array, matrix:Matrix = null, spreadMethod:String = "pad", interpolationMethod:String = "rgb", focalPointRatio:Number = 0):void
Specifies a gradient to use for the stroke when drawing lines. | Graphics | ||
Specifies a shader to use for the line stroke when drawing lines. | Graphics | ||
lineStyle(thickness:Number = NaN, color:uint = 0, alpha:Number = 1.0, pixelHinting:Boolean = false, scaleMode:String = "normal", caps:String = null, joints:String = null, miterLimit:Number = 3):void
Specifies a line style used for subsequent calls to
Graphics methods such as the lineTo() method or the drawCircle() method. | Graphics | ||
Draws a line using the current line style from the current drawing position to (x, y);
the current drawing position is then set to (x, y). | Graphics | ||
Moves the current drawing position to (x, y). | Graphics | ||
 |
Indicates whether the specified property exists and is enumerable. | Object | |
 |
Sets the availability of a dynamic property for loop operations. | Object | |
 |
Returns the string representation of this object, formatted according to locale-specific conventions. | Object | |
 |
Returns the string representation of the specified object. | Object | |
 |
Returns the primitive value of the specified object. | Object | |
| beginBitmapFill | () | method |
public function beginBitmapFill(bitmap:BitmapData, matrix:Matrix = null, repeat:Boolean = true, smooth:Boolean = false):void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | AIR 1.0 Flash Player 9 |
Fills a drawing area with a bitmap image. The bitmap can be repeated or tiled to fill
the area. The fill remains in effect until you call the beginFill(),
beginBitmapFill(), beginGradientFill(), or beginShaderFill() method.
Calling the clear() method clears the fill.
The application renders the fill whenever three or more points are drawn, or when
the endFill() method is called.
Parameters
bitmap:BitmapData — A transparent or opaque bitmap image that contains the bits to be displayed.
| |
matrix:Matrix (default = null)
matrix = new flash.geom.Matrix();
matrix.rotate(Math.PI / 4);
| |
repeat:Boolean (default = true)true, the bitmap image repeats in a tiled pattern. If
false, the bitmap image does not repeat, and the edges of the bitmap are
used for any fill area that extends beyond the bitmap.
For example, consider the following bitmap (a 20 x 20-pixel checkerboard pattern):
When
When
| |
smooth:Boolean (default = false)false, upscaled bitmap images are rendered by using a
nearest-neighbor algorithm and look pixelated. If true, upscaled
bitmap images are rendered by using a bilinear algorithm. Rendering by using the nearest
neighbor algorithm is faster.
|
See also
image1.jpg) that is rotated and repeated to fill in a rectangle.
image1.jpg) is loaded using the Loader and URLRequest objects.
Here the file is in the same directory as the SWF file. The SWF file needs to be compiled with Local Playback
Security set to Access Local Files Only.Event is complete), the drawImage() method is called.
The ioErrorHandler() method writes a trace comment if the image was not loaded properly.drawImage() method, a BitmapData object is instantiated and its width and height
are set to the image (image1.jpg). Then the source image is drawn into the BitmapData
object. Next, a rectangle is drawn in the mySprite Sprite object and the BitmapData object is used to
fill it. Using a Matrix object, the beginBitmapFill() method rotates the image 45 degrees,
then it begins filling the rectangle with the image until it is finished.
package {
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.display.BitmapData;
import flash.display.Loader;
import flash.net.URLRequest;
import flash.events.Event;
import flash.events.IOErrorEvent;
import flash.geom.Matrix;
public class Graphics_beginBitmapFillExample extends Sprite {
private var url:String = "image1.jpg";
private var loader:Loader = new Loader();
public function Graphics_beginBitmapFillExample() {
var request:URLRequest = new URLRequest(url);
loader.load(request);
loader.contentLoaderInfo.addEventListener(Event.COMPLETE, drawImage);
loader.contentLoaderInfo.addEventListener(IOErrorEvent.IO_ERROR, ioErrorHandler);
}
private function drawImage(event:Event):void {
var mySprite:Sprite = new Sprite();
var myBitmap:BitmapData = new BitmapData(loader.width, loader.height, false);
myBitmap.draw(loader, new Matrix());
var matrix:Matrix = new Matrix();
matrix.rotate(Math.PI/4);
mySprite.graphics.beginBitmapFill(myBitmap, matrix, true);
mySprite.graphics.drawRect(100, 50, 200, 90);
mySprite.graphics.endFill();
addChild(mySprite);
}
private function ioErrorHandler(event:IOErrorEvent):void {
trace("Unable to load image: " + url);
}
}
}
| beginFill | () | method |
public function beginFill(color:uint, alpha:Number = 1.0):void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | AIR 1.0 Flash Player 9 |
Specifies a simple one-color fill that subsequent calls to other
Graphics methods (such as lineTo() or drawCircle()) use when drawing.
The fill remains in effect until you call the beginFill(),
beginBitmapFill(), beginGradientFill(), or beginShaderFill() method.
Calling the clear() method clears the fill.
The application renders the fill whenever three or more points are drawn, or when
the endFill() method is called.
Parameters
color:uint — The color of the fill (0xRRGGBB).
| |
alpha:Number (default = 1.0) |
See also
| beginGradientFill | () | method |
public function beginGradientFill(type:String, colors:Array, alphas:Array, ratios:Array, matrix:Matrix = null, spreadMethod:String = "pad", interpolationMethod:String = "rgb", focalPointRatio:Number = 0):void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | AIR 1.0 Flash Player 9 |
Specifies a gradient fill used by subsequent calls to other
Graphics methods (such as lineTo() or drawCircle()) for the object.
The fill remains in effect until you call the beginFill(),
beginBitmapFill(), beginGradientFill(), or beginShaderFill() method.
Calling the clear() method clears the fill.
The application renders the fill whenever three or more points are drawn, or when
the endFill() method is called.
Parameters
type:String — A value from the GradientType class that
specifies which gradient type to use: GradientType.LINEAR or
GradientType.RADIAL.
| |||||||||
colors:Array — An array of RGB hexadecimal color values used in the gradient; for example,
red is 0xFF0000, blue is 0x0000FF, and so on. You can specify up to 15 colors.
For each color, specify a corresponding value in the alphas and ratios parameters.
| |||||||||
alphas:Array — An array of alpha values for the corresponding colors in the colors array;
valid values are 0 to 1. If the value is less than 0, the default is 0. If the value is
greater than 1, the default is 1.
| |||||||||
ratios:Array — An array of color distribution ratios; valid values are 0-255. This value
defines the percentage of the width where the color is sampled at 100%. The value 0 represents
the left position in the gradient box, and 255 represents the right position in the
gradient box.
Note: This value represents positions in the gradient box, not the
coordinate space of the final gradient, which can be wider or thinner than the gradient box.
Specify a value for each value in the For example, for a linear gradient that includes two colors, blue and green, the
following example illustrates the placement of the colors in the gradient based on different values
in the
The values in the array must increase sequentially; for example,
| |||||||||
matrix:Matrix (default = null)createGradientBox() method, which lets you conveniently set up
the matrix for use with the beginGradientFill() method.
| |||||||||
spreadMethod:String (default = "pad")SpreadMethod.PAD,
SpreadMethod.REFLECT, or SpreadMethod.REPEAT.
For example, consider a simple linear gradient between two colors:
import flash.geom.*
import flash.display.*
var fillType:String = GradientType.LINEAR;
var colors:Array = [0xFF0000, 0x0000FF];
var alphas:Array = [1, 1];
var ratios:Array = [0x00, 0xFF];
var matr:Matrix = new Matrix();
matr.createGradientBox(20, 20, 0, 0, 0);
var spreadMethod:String = SpreadMethod.PAD;
this.graphics.beginGradientFill(fillType, colors, alphas, ratios, matr, spreadMethod);
this.graphics.drawRect(0,0,100,100);
This example uses
If you use
If you use
| |||||||||
interpolationMethod:String (default = "rgb")InterpolationMethod.LINEAR_RGB or
InterpolationMethod.RGB
For example, consider a simple linear gradient between two colors (with the
| |||||||||
focalPointRatio:Number (default = 0)focalPointRatio set to 0.75:
|
ArgumentError — If the type parameter is not valid.
|
See also
| beginShaderFill | () | method |
public function beginShaderFill(shader:Shader, matrix:Matrix = null):void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | Flash Player 10, AIR 1.5 |
Specifies a shader fill used by subsequent calls to other Graphics methods
(such as lineTo() or drawCircle()) for the object.
The fill remains in effect until you call the beginFill(),
beginBitmapFill(), beginGradientFill(), or beginShaderFill() method.
Calling the clear() method clears the fill.
The application renders the fill whenever three or more points are drawn, or when
the endFill() method is called.
Parameters
shader:Shader — The shader to use for the fill. This Shader instance is not required to
specify an image input. However, if an image input is specified in the shader, the input
must be provided manually. To specify the input, set the input property
of the corresponding ShaderInput
property of the Shader.data property.
When you pass a Shader instance as an argument the shader is copied internally. The drawing fill operation uses that internal copy, not a reference to the original shader. Any changes made to the shader, such as changing a parameter value, input, or bytecode, are not applied to the copied shader that's used for the fill. | |
matrix:Matrix (default = null)
matrix = new flash.geom.Matrix();
matrix.rotate(Math.PI / 4);
The coordinates received in the shader are based on the matrix that is specified
for the |
ArgumentError — When the shader output type is not compatible with this operation
(the shader must specify a pixel3 or pixel4
output).
| |
ArgumentError — When the shader specifies an image input that isn't provided.
| |
ArgumentError — When a ByteArray or Vector.<Number> instance is used as
an input and the width
and height properties aren't specified for the
ShaderInput, or the specified values don't match the amount of
data in the input object. See the ShaderInput.input
property for more information.
|
See also
| clear | () | method |
public function clear():void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | AIR 1.0 Flash Player 9 |
Clears the graphics that were drawn to this Graphics object, and resets fill and line style settings.
| copyFrom | () | method |
public function copyFrom(sourceGraphics:Graphics):void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | Flash Player 10, AIR 1.5 |
Copies all of drawing commands from the source Graphics object into the calling Graphics object.
Parameters
sourceGraphics:Graphics — The Graphics object from which to copy the drawing commands.
|
| curveTo | () | method |
public function curveTo(controlX:Number, controlY:Number, anchorX:Number, anchorY:Number):void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | AIR 1.0 Flash Player 9 |
Draws a curve using the current line style from the current drawing position
to (anchorX, anchorY) and using the control point that (controlX,
controlY) specifies. The current drawing position is then set to
(anchorX, anchorY). If the movie clip in which you are
drawing contains content created with the Flash drawing tools, calls to the
curveTo() method are drawn underneath this content. If you call the
curveTo() method before any calls to the moveTo() method,
the default of the current drawing position is (0, 0). If any of the parameters are
missing, this method fails and the current drawing position is not changed.
The curve drawn is a quadratic Bezier curve. Quadratic Bezier curves consist of two anchor points and one control point. The curve interpolates the two anchor points and curves toward the control point.
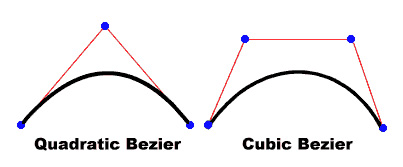
Parameters
controlX:Number — A number that specifies the horizontal position of the control
point relative to the registration point of the parent display object.
| |
controlY:Number — A number that specifies the vertical position of the control
point relative to the registration point of the parent display object.
| |
anchorX:Number — A number that specifies the horizontal position of the next anchor
point relative to the registration point of the parent display object.
| |
anchorY:Number — A number that specifies the vertical position of the next anchor
point relative to the registration point of the parent display object.
|
Draw four curves to produce a circle and fill it green.
Note that due to the nature of the quadratic Bezier equation, this is not a perfect circle.
The best way to draw a circle is to use the Graphics class's drawCircle() method.
package {
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.display.Shape;
public class Graphics_curveToExample1 extends Sprite
{
public function Graphics_curveToExample1():void
{
var roundObject:Shape = new Shape();
roundObject.graphics.beginFill(0x00FF00);
roundObject.graphics.moveTo(250, 0);
roundObject.graphics.curveTo(300, 0, 300, 50);
roundObject.graphics.curveTo(300, 100, 250, 100);
roundObject.graphics.curveTo(200, 100, 200, 50);
roundObject.graphics.curveTo(200, 0, 250, 0);
roundObject.graphics.endFill();
this.addChild(roundObject);
}
}
}
curveTo() method.
Two curve lines of 1 pixel are drawn and the space in between is filled white. The moveTo()
method is used to position the current drawing position to coordinates (100, 100). The first curve moves the drawing
position to (100, 200), its destination point. The second curve returns the position back to
the starting position (100, 100), its destination point. The horizontal control points determine
the different curve sizes.
package {
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.display.Shape;
public class Graphics_curveToExample2 extends Sprite
{
public function Graphics_curveToExample2() {
var newMoon:Shape = new Shape();
newMoon.graphics.lineStyle(1, 0);
newMoon.graphics.beginFill(0xFFFFFF);
newMoon.graphics.moveTo(100, 100);
newMoon.graphics.curveTo(30, 150, 100, 200);
newMoon.graphics.curveTo(50, 150, 100, 100);
graphics.endFill();
this.addChild(newMoon);
}
}
}
| drawCircle | () | method |
public function drawCircle(x:Number, y:Number, radius:Number):void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | AIR 1.0 Flash Player 9 |
Draws a circle. Set the line style, fill, or both before
you call the drawCircle() method, by calling the linestyle(),
lineGradientStyle(), beginFill(), beginGradientFill(),
or beginBitmapFill() method.
Parameters
x:Number — The x location of the center of the circle relative to the
registration point of the parent display object (in pixels).
| |
y:Number — The y location of the center of the circle relative to the
registration point of the parent display object (in pixels).
| |
radius:Number — The radius of the circle (in pixels).
|
See also
| drawEllipse | () | method |
public function drawEllipse(x:Number, y:Number, width:Number, height:Number):void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | AIR 1.0 Flash Player 9 |
Draws an ellipse. Set the line style, fill, or both before
you call the drawEllipse() method, by calling the linestyle(),
lineGradientStyle(), beginFill(), beginGradientFill(),
or beginBitmapFill() method.
Parameters
x:Number — The x location of the top-left of the bounding-box of the ellipse relative to the
registration point of the parent display object (in pixels).
| |
y:Number — The y location of the top left of the bounding-box of the ellipse relative to the
registration point of the parent display object (in pixels).
| |
width:Number — The width of the ellipse (in pixels).
| |
height:Number — The height of the ellipse (in pixels).
|
See also
drawEgg() to draw three different sized eggs
(three sizes of ellipses), depending on the eggSize parameter.
drawEgg() and passes the horizontal and vertical parameters for
where the egg should be drawn, plus the type of egg (eggSize). (The height and width of the
eggs (the ellipses) can be used to decide where to display them.)drawEgg() draws the different size ellipses and fills them white using
beginFill() method. There is no advance error handling written for his function.
package {
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.display.Shape;
public class Graphics_drawEllipseExample extends Sprite
{
public static const SMALL:uint = 0;
public static const MEDIUM:uint = 1;
public static const LARGE:uint = 2;
public function Graphics_drawEllipseExample()
{
drawEgg(SMALL, 0, 100);
drawEgg(MEDIUM, 100, 60);
drawEgg(LARGE, 250, 35);
}
public function drawEgg(eggSize:uint, x:Number, y:Number):void {
var myEgg:Shape = new Shape();
myEgg.graphics.beginFill(0xFFFFFF);
myEgg.graphics.lineStyle(1);
switch(eggSize) {
case SMALL:
myEgg.graphics.drawEllipse(x, y, 60, 70);
break;
case MEDIUM:
myEgg.graphics.drawEllipse(x, y, 120, 150);
break;
case LARGE:
myEgg.graphics.drawEllipse(x, y, 150, 200);
break;
default:
trace ("Wrong size! There is no egg.");
break;
}
myEgg.graphics.endFill();
this.addChild(myEgg);
}
}
}
| drawGraphicsData | () | method |
public function drawGraphicsData(graphicsData:Vector.<IGraphicsData>):void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | Flash Player 10, AIR 1.5 |
Submits a series of IGraphicsData instances for drawing. This method accepts a Vector containing objects including paths, fills, and strokes that implement the IGraphicsData interface. A Vector of IGraphicsData instances can refer to a part of a shape, or a complex fully defined set of data for rendering a complete shape.
Graphics paths can contain other graphics paths. If the graphicsData Vector
includes a path, that path and all its sub-paths are rendered during this operation.
Parameters
graphicsData:Vector.<IGraphicsData> — A Vector containing graphics objects, each of which much implement the IGraphicsData interface.
|
See also
drawGraphicsData() command to render the shape.
package{
import flash.display.*;
import flash.geom.*;
public class DrawGraphicsDataExample extends Sprite {
public function DrawGraphicsDataExample(){
// establish the fill properties
var myFill:GraphicsGradientFill = new GraphicsGradientFill();
myFill.colors = [0xEEFFEE, 0x0000FF];
myFill.matrix = new Matrix();
myFill.matrix.createGradientBox(100, 100, 0);
// establish the stroke properties
var myStroke:GraphicsStroke = new GraphicsStroke(2);
myStroke.fill = new GraphicsSolidFill(0x000000);
// establish the path properties
var myPath:GraphicsPath = new GraphicsPath(new Vector.<int>(), new Vector.<Number>());
myPath.commands.push(1,2,2,2,2);
myPath.data.push(10,10, 10,100, 100,100, 100,10, 10,10);
// populate the IGraphicsData Vector array
var myDrawing:Vector.<IGraphicsData> = new Vector.<IGraphicsData>();
myDrawing.push(myFill, myStroke, myPath);
// render the drawing
graphics.drawGraphicsData(myDrawing);
}
}
}
| drawPath | () | method |
public function drawPath(commands:Vector.<int>, data:Vector.<Number>, winding:String = "evenOdd"):void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | Flash Player 10, AIR 1.5 |
Submits a series of commands for drawing. The drawPath() method uses vector arrays to consolidate
individual moveTo(), lineTo(), and curveTo() drawing commands
into a single call. The drawPath() method parameters combine drawing commands with x- and y-coordinate
value pairs and a drawing direction. The drawing commands are values from the GraphicsPathCommand class. The
x- and y-coordinate value pairs are Numbers in an array where each pair defines a coordinate location. The drawing
direction is a value from the GraphicsPathWinding class.
Generally, drawings render faster with drawPath() than with
a series of individual lineTo() and curveTo() methods.
The drawPath() method uses a uses a floating computation so rotation and scaling
of shapes is more accurate and gives better results. However, curves submitted using the
drawPath() method can have small sub-pixel alignment errors when used in conjunction
with the lineTo() and curveTo() methods.
The drawPath() method also uses slightly different rules for filling and drawing lines.
They are:
Parameters
commands:Vector.<int> — A Vector of integers representing commands defined by the GraphicsPathCommand class. The
GraphicsPathCommand class maps commands to numeric identifiers for this vector array.
| |
data:Vector.<Number> — A Vector of Numbers where each pair of numbers is treated as a coordinate location (an x, y pair).
The x- and y-coordinate value pairs are not Point objects; the data vector is
a series of numbers where each group of two numbers represents a coordinate location.
| |
winding:String (default = "evenOdd") |
See also
drawPath() method to render a blue star. The first Vector, star_commands, contains a series of
integers representing drawing commands from the flash.display.GraphicsPathCommand class,
where the value 1 is a MoveTo() command and the value 2 is a LineTo()
command. The second Vector, star_coord, contains 5 sets of x- and y-coordinate pairs.
The drawPath() method matches the commands with the positions to draw a star.
package{
import flash.display.*;
public class DrawPathExample extends Sprite {
public function DrawPathExample(){
var star_commands:Vector.<int> = new Vector.<int>(5, true);
star_commands[0] = 1;
star_commands[1] = 2;
star_commands[2] = 2;
star_commands[3] = 2;
star_commands[4] = 2;
var star_coord:Vector.<Number> = new Vector.<Number>(10, true);
star_coord[0] = 66; //x
star_coord[1] = 10; //y
star_coord[2] = 23;
star_coord[3] = 127;
star_coord[4] = 122;
star_coord[5] = 50;
star_coord[6] = 10;
star_coord[7] = 49;
star_coord[8] = 109;
star_coord[9] = 127;
graphics.beginFill(0x003366);
graphics.drawPath(star_commands, star_coord);
}
}
}
push() statement:
package{
import flash.display.*;
public class DrawPathExample extends Sprite {
public function DrawPathExample(){
var star_commands:Vector.<int> = new Vector.<int>();
star_commands.push(1, 2, 2, 2, 2);
var star_coord:Vector.<Number> = new Vector.<Number>();
star_coord.push(66,10, 23,127, 122,50, 10,49, 109,127);
graphics.beginFill(0x003366);
graphics.drawPath(star_commands, star_coord);
}
}
}
drawPath() method uses the even-odd winding type. So,
the center of the star is not filled. Specify the non-zero winding type for the third parameter
and it fills the center of the star:
graphics.drawPath(star_commands, star_coord, GraphicsPathWinding.NON_ZERO);
| drawRect | () | method |
public function drawRect(x:Number, y:Number, width:Number, height:Number):void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | AIR 1.0 Flash Player 9 |
Draws a rectangle. Set the line style, fill, or both before
you call the drawRect() method, by calling the linestyle(),
lineGradientStyle(), beginFill(), beginGradientFill(),
or beginBitmapFill() method.
Parameters
x:Number — A number indicating the horizontal position relative to the
registration point of the parent display object (in pixels).
| |
y:Number — A number indicating the vertical position relative to the
registration point of the parent display object (in pixels).
| |
width:Number — The width of the rectangle (in pixels).
| |
height:Number — The height of the rectangle (in pixels).
|
ArgumentError — If the width or height parameters
are not a number (Number.NaN).
|
See also
| drawRoundRect | () | method |
public function drawRoundRect(x:Number, y:Number, width:Number, height:Number, ellipseWidth:Number, ellipseHeight:Number = NaN):void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | AIR 1.0 Flash Player 9 |
Draws a rounded rectangle. Set the line style, fill, or both before
you call the drawRoundRect() method, by calling the linestyle(),
lineGradientStyle(), beginFill(), beginGradientFill(), or
beginBitmapFill() method.
Parameters
x:Number — A number indicating the horizontal position relative to the
registration point of the parent display object (in pixels).
| |
y:Number — A number indicating the vertical position relative to the
registration point of the parent display object (in pixels).
| |
width:Number — The width of the round rectangle (in pixels).
| |
height:Number — The height of the round rectangle (in pixels).
| |
ellipseWidth:Number — The width of the ellipse used to draw the rounded corners (in pixels).
| |
ellipseHeight:Number (default = NaN)ellipseWidth parameter.
|
ArgumentError — If the width, height, ellipseWidth
or ellipseHeight parameters are not a number (Number.NaN).
|
See also
| drawTriangles | () | method |
public function drawTriangles(vertices:Vector.<Number>, indices:Vector.<int> = null, uvtData:Vector.<Number> = null, culling:String = "none"):void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | Flash Player 10, AIR 1.5 |
Renders a set of triangles, typically to distort bitmaps and give them a three-dimensional appearance. The
drawTriangles() method maps either the current fill, or a bitmap fill, to the
triangle faces using a set of (u,v) coordinates.
Any type of fill can be used, but if the fill has a transform matrix that transform matrix is ignored.
A uvtData parameter improves texture mapping when a bitmap fill is used.
Parameters
vertices:Vector.<Number> — A Vector of Numbers where each pair of numbers is treated as a coordinate location (an x, y pair). The
vertices parameter is required.
| |
indices:Vector.<int> (default = null)indexes parameter
is null then every three vertices (six x,y pairs in the vertices Vector) defines a triangle.
Otherwise each index refers to a vertex, which is a pair of numbers in the vertices Vector.
For example indexes[1] refers to (vertices[2], vertices[3]).
The indexes parameter is optional, but indexes generally reduce the amount of data submitted
and the amount of data computed.
| |
uvtData:Vector.<Number> (default = null)If the length of this vector is twice the length of the If the length of this vector is three times the length of the If the | |
culling:String (default = "none") |
See also
| endFill | () | method |
public function endFill():void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | AIR 1.0 Flash Player 9 |
Applies a fill to the lines and curves that were added since the last call to the
beginFill(), beginGradientFill(), or
beginBitmapFill() method. Flash uses the fill that was specified in the previous
call to the beginFill(), beginGradientFill(), or beginBitmapFill()
method. If the current drawing position does not equal the previous position specified in a
moveTo() method and a fill is defined, the path is closed with a line and then
filled.
See also
| lineBitmapStyle | () | method |
public function lineBitmapStyle(bitmap:BitmapData, matrix:Matrix = null, repeat:Boolean = true, smooth:Boolean = false):void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | Flash Player 10, AIR 1.5 |
Specifies a bitmap to use for the line stroke when drawing lines.
The bitmap line style is used for subsequent calls to Graphics
methods such as the lineTo() method or the drawCircle() method.
The line style remains in effect until you call the lineStyle() or
lineGradientStyle() methods, or the lineBitmapStyle() method
again with different parameters.
You can call the lineBitmapStyle() method in the middle of drawing a path
to specify different styles for different line segments within a path.
Call the lineStyle() method before you call the
lineBitmapStyle() method to enable a stroke, or else the value of the line style
is undefined.
Calls to the clear() method set the line style back to undefined.
Parameters
bitmap:BitmapData — The bitmap to use for the line stroke.
| |
matrix:Matrix (default = null) | |
repeat:Boolean (default = true) | |
smooth:Boolean (default = false) |
See also
| lineGradientStyle | () | method |
public function lineGradientStyle(type:String, colors:Array, alphas:Array, ratios:Array, matrix:Matrix = null, spreadMethod:String = "pad", interpolationMethod:String = "rgb", focalPointRatio:Number = 0):void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | AIR 1.0 Flash Player 9 |
Specifies a gradient to use for the stroke when drawing lines.
The gradient line style is used for subsequent calls to Graphics
methods such as the lineTo() methods or the drawCircle() method.
The line style remains in effect until you call the lineStyle() or
lineBitmapStyle() methods, or the lineGradientStyle() method
again with different parameters.
You can call the lineGradientStyle() method in the middle of drawing a path
to specify different styles for different line segments within a path.
Call the lineStyle() method before you call the
lineGradientStyle() method to enable a stroke, or else the value of the line style
is undefined.
Calls to the clear() method set the line style back to undefined.
Parameters
type:String — A value from the GradientType class that
specifies which gradient type to use, either GradientType.LINEAR or GradientType.RADIAL.
| |||||||||
colors:Array — An array of RGB hex color values to be used in the gradient (for example,
red is 0xFF0000, blue is 0x0000FF, and so on).
| |||||||||
alphas:Array — An array of alpha values for the corresponding colors in the colors array;
valid values are 0 to 1. If the value is less than 0, the default is 0. If the value is
greater than 1, the default is 1.
| |||||||||
ratios:Array — An array of color distribution ratios; valid values are from 0 to 255. This value
defines the percentage of the width where the color is sampled at 100%. The value 0 represents
the left position in the gradient box, and 255 represents the right position in the
gradient box. This value represents positions in the gradient box, not the
coordinate space of the final gradient, which can be wider or thinner than the gradient box.
Specify a value for each value in the colors parameter.
For example, for a linear gradient that includes two colors, blue and green, the
following figure illustrates the placement of the colors in the gradient based on different values
in the
The values in the array must increase, sequentially; for example,
| |||||||||
matrix:Matrix (default = null)createGradientBox() method, which lets you conveniently set up
the matrix for use with the lineGradientStyle() method.
| |||||||||
spreadMethod:String (default = "pad")
| |||||||||
interpolationMethod:String (default = "rgb")spreadMethod
parameter set to SpreadMethod.REFLECT). The different interpolation methods affect
the appearance as follows:
| |||||||||
focalPointRatio:Number (default = 0)focalPointRatio of -0.75:
|
See also
The method createGradientBox() from the Matrix class is used to define the
gradient box to 200 width and 40 height. The thickness of line is set to 5 pixels. Thickness of the stroke
must be defined for lineGradientStyle() method. The gradient is set to linear. Colors for the
gradient are set to red, green, and blue. Transparency (alpha value) for the colors is set to 1 (opaque).
The distribution of gradient is even, where the colors are sampled at 100% at 0 (left-hand position in the
gradient box), 128 (middle in the box) and 255 (right-hand position in the box). The width of the rectangle
encompasses all the spectrum of the gradient, while the circle encompasses 50% from the middle of the spectrum.
package {
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.display.Shape;
import flash.geom.Matrix;
import flash.display.GradientType;
public class Graphics_lineGradientStyleExample extends Sprite
{
public function Graphics_lineGradientStyleExample()
{
var myShape:Shape = new Shape();
var gradientBoxMatrix:Matrix = new Matrix();
gradientBoxMatrix.createGradientBox(200, 40, 0, 0, 0);
myShape.graphics.lineStyle(5);
myShape.graphics.lineGradientStyle(GradientType.LINEAR, [0xFF0000,
0x00FF00, 0x0000FF], [1, 1, 1], [0, 128, 255], gradientBoxMatrix);
myShape.graphics.drawRect(0, 0, 200, 40);
myShape.graphics.drawCircle(100, 120, 50);
this.addChild(myShape);
}
}
}
| lineShaderStyle | () | method |
public function lineShaderStyle(shader:Shader, matrix:Matrix = null):void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | Flash Player 10, AIR 1.5 |
Specifies a shader to use for the line stroke when drawing lines.
The shader line style is used for subsequent calls to Graphics
methods such as the lineTo() method or the drawCircle() method.
The line style remains in effect until you call the lineStyle() or
lineGradientStyle() methods, or the lineBitmapStyle() method
again with different parameters.
You can call the lineShaderStyle() method in the middle of drawing a path
to specify different styles for different line segments within a path.
Call the lineStyle() method before you call the
lineShaderStyle() method to enable a stroke, or else the value of the line style
is undefined.
Calls to the clear() method set the line style back to undefined.
Parameters
shader:Shader — The shader to use for the line stroke.
| |
matrix:Matrix (default = null) |
See also
| lineStyle | () | method |
public function lineStyle(thickness:Number = NaN, color:uint = 0, alpha:Number = 1.0, pixelHinting:Boolean = false, scaleMode:String = "normal", caps:String = null, joints:String = null, miterLimit:Number = 3):void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | AIR 1.0 Flash Player 9 |
Specifies a line style used for subsequent calls to
Graphics methods such as the lineTo() method or the drawCircle() method.
The line style remains in effect until you call the lineGradientStyle()
method, the lineBitmapStyle() method, or the lineStyle() method with different parameters.
You can call the lineStyle() method in the middle of drawing a path to specify different
styles for different line segments within the path.
Note: Calls to the clear() method set the line style back to
undefined.
Parameters
thickness:Number (default = NaN) | |||||||||||
color:uint (default = 0) | |||||||||||
alpha:Number (default = 1.0) | |||||||||||
pixelHinting:Boolean (default = false)pixelHinting set to true, line widths are adjusted
to full pixel widths. With pixelHinting set to false, disjoints can
appear for curves and straight lines. For example, the following illustrations show how
Flash Player or Adobe AIR renders two rounded rectangles that are identical, except that the
pixelHinting parameter used in the lineStyle() method is set
differently (the images are scaled by 200%, to emphasize the difference):
If a value is not supplied, the line does not use pixel hinting. | |||||||||||
scaleMode:String (default = "normal")
| |||||||||||
caps:String (default = null)CapsStyle.NONE, CapsStyle.ROUND, and CapsStyle.SQUARE.
If a value is not indicated, Flash uses round caps.
For example, the following illustrations show the different
| |||||||||||
joints:String (default = null)JointStyle.BEVEL, JointStyle.MITER, and JointStyle.ROUND.
If a value is not indicated, Flash uses round joints.
For example, the following illustrations show the different
Note: For | |||||||||||
miterLimit:Number (default = 3)jointStyle
is set to "miter". The
miterLimit value represents the length that a miter can extend beyond the point
at which the lines meet to form a joint. The value expresses a factor of the line
thickness. For example, with a miterLimit factor of 2.5 and a
thickness of 10 pixels, the miter is cut off at 25 pixels.
For example, consider the following angled lines, each drawn with a
Notice that a given
|
See also
getStyle() method.
| lineTo | () | method |
public function lineTo(x:Number, y:Number):void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | AIR 1.0 Flash Player 9 |
Draws a line using the current line style from the current drawing position to (x, y);
the current drawing position is then set to (x, y).
If the display object in which you are drawing contains content that was created with
the Flash drawing tools, calls to the lineTo() method are drawn underneath the content. If
you call lineTo() before any calls to the moveTo() method, the
default position for the current drawing is (0, 0). If any of the parameters are missing, this
method fails and the current drawing position is not changed.
Parameters
x:Number — A number that indicates the horizontal position relative to the
registration point of the parent display object (in pixels).
| |
y:Number — A number that indicates the vertical position relative to the
registration point of the parent display object (in pixels).
|
lineTo() method, starting at
pixels (100, 100).
The line thickness is set to 10 pixels, color is gold and opaque, caps at the end of lines
is set to none (since all lines are jointed), and the joint between the lines is set to
MITER with miter limit set to 10, to have sharp, pointed corners.
package {
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.display.LineScaleMode;
import flash.display.CapsStyle;
import flash.display.JointStyle;
import flash.display.Shape;
public class Graphics_lineToExample extends Sprite {
public function Graphics_lineToExample() {
var trapezoid:Shape = new Shape();
trapezoid.graphics.lineStyle(10, 0xFFD700, 1, false, LineScaleMode.VERTICAL,
CapsStyle.NONE, JointStyle.MITER, 10);
trapezoid.graphics.moveTo(100, 100);
trapezoid.graphics.lineTo(120, 50);
trapezoid.graphics.lineTo(200, 50);
trapezoid.graphics.lineTo(220, 100);
trapezoid.graphics.lineTo(100, 100);
this.addChild(trapezoid);
}
}
}
| moveTo | () | method |
public function moveTo(x:Number, y:Number):void| Language Version: | ActionScript 3.0 |
| Runtime Versions: | AIR 1.0 Flash Player 9 |
Moves the current drawing position to (x, y). If any of the parameters
are missing, this method fails and the current drawing position is not changed.
Parameters
x:Number — A number that indicates the horizontal position relative to the
registration point of the parent display object (in pixels).
| |
y:Number — A number that indicates the vertical position relative to the
registration point of the parent display object (in pixels).
|
moveTo() and lineTo() methods.
Using the lineStyle() method, the line thickness is set to 3 pixels. It is also set not
to scale. Color is set to red with 25 percent opacity. The CapsStyle property is set to
square (the default is round).
Since Graphics_moveToExample is an instance of the Sprite class, it has access
to all the Graphics class methods. The Graphics class methods can be used to directly draw on the
Graphic_moveToExample Sprite object. However, not putting the vector drawing object in a
Shape limits the way they can be managed, moved, or changed.
package {
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.display.CapsStyle;
import flash.display.LineScaleMode;
public class Graphics_moveToExample extends Sprite
{
public function Graphics_moveToExample() {
graphics.lineStyle(3, 0x990000, 0.25, false,
LineScaleMode.NONE, CapsStyle.SQUARE);
graphics.moveTo(10, 20);
graphics.lineTo(20, 20);
graphics.moveTo(30, 20);
graphics.lineTo(50, 20);
graphics.moveTo(60, 20);
graphics.lineTo(80, 20);
graphics.moveTo(90, 20);
graphics.lineTo(110, 20);
graphics.moveTo(120, 20);
graphics.lineTo(130, 20);
}
}
}
size property for later use in determining the size of each shape.
package {
import flash.display.DisplayObject;
import flash.display.Graphics;
import flash.display.Shape;
import flash.display.Sprite;
public class GraphicsExample extends Sprite {
private var size:uint = 80;
private var bgColor:uint = 0xFFCC00;
private var borderColor:uint = 0x666666;
private var borderSize:uint = 0;
private var cornerRadius:uint = 9;
private var gutter:uint = 5;
public function GraphicsExample() {
doDrawCircle();
doDrawRoundRect();
doDrawRect();
refreshLayout();
}
private function refreshLayout():void {
var ln:uint = numChildren;
var child:DisplayObject;
var lastChild:DisplayObject = getChildAt(0);
lastChild.x = gutter;
lastChild.y = gutter;
for (var i:uint = 1; i < ln; i++) {
child = getChildAt(i);
child.x = gutter + lastChild.x + lastChild.width;
child.y = gutter;
lastChild = child;
}
}
private function doDrawCircle():void {
var child:Shape = new Shape();
var halfSize:uint = Math.round(size / 2);
child.graphics.beginFill(bgColor);
child.graphics.lineStyle(borderSize, borderColor);
child.graphics.drawCircle(halfSize, halfSize, halfSize);
child.graphics.endFill();
addChild(child);
}
private function doDrawRoundRect():void {
var child:Shape = new Shape();
child.graphics.beginFill(bgColor);
child.graphics.lineStyle(borderSize, borderColor);
child.graphics.drawRoundRect(0, 0, size, size, cornerRadius);
child.graphics.endFill();
addChild(child);
}
private function doDrawRect():void {
var child:Shape = new Shape();
child.graphics.beginFill(bgColor);
child.graphics.lineStyle(borderSize, borderColor);
child.graphics.drawRect(0, 0, size, size);
child.graphics.endFill();
addChild(child);
}
}
}